| Part of a series on the |
| Wildlife of Great Britain |
|---|
 |
The reptiles of Great Britain include three native snakes and three native lizards. A number of sea turtles visit Great Britain's shores. There are also at least seven introduced reptile species.
Snakes (Serpentes)
| Image | Name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
_(7345075454).jpg.webp) |
Common adder, Vipera berus[1] | 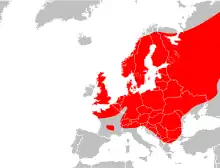 |
.jpg.webp) |
Barred grass snake, Natrix helvetica[2][lower-alpha 1] | .png.webp) |
_(7345077432).jpg.webp) |
Smooth snake, Coronella austriaca[4] | 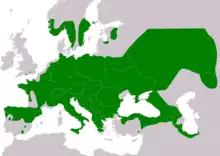 |
Lizards (Lacertilia)
| Image | Name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
.jpg.webp) |
Slow worm, Anguis fragilis[5][6] | 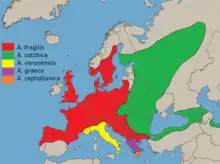 |
.jpeg.webp) |
Viviparous lizard, Zootoca vivipara[7] |  |
 |
Sand lizard, Lacerta agilis |  |
Sea turtles (Chelonioidea)
| Image | Name | Distribution | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Leatherback sea turtle, Dermochelys coriacea | 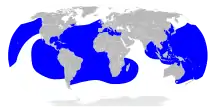 |
Foraging[8] |
 |
Loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta | 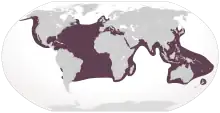 |
Vagrant[9] |
.jpg.webp) |
Green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas | 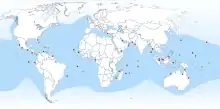 |
Vagrant[10] |
 |
Hawksbill sea turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata | 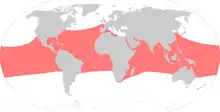 |
Vagrant[10] |
 |
Kemp's ridley sea turtle, Lepidochelys kempii | 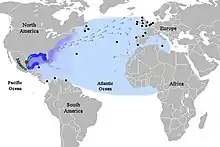 |
Vagrant[10] |
 |
Olive ridley sea turtle, Lepidochelys olivacea | 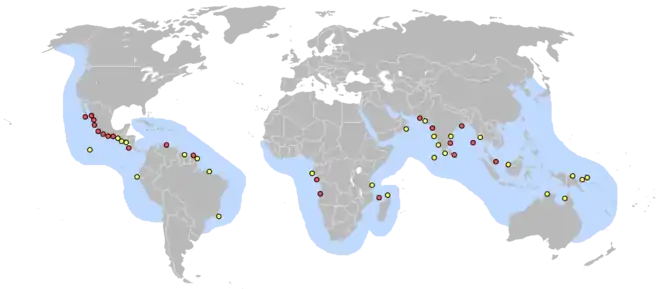 |
Vagrant[11] |
Introduced species
- Red-eared slider, Trachemys scripta elegans[12][13]
- European pond terrapin, Emys orbicularis[14]
- Common wall lizard, Podarcis muralis[15]
- Western green lizard, Lacerta bilineata[16]
- Aesculapian snake, Zamenis longissimus[17][18][19]
- Grass snake, Natrix natrix[20]
See also
References
- ↑ "Adder". Woodland Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- 1 2 Carolin Kindler; Maxime Chèvre; Sylvain Ursenbacher; Wolfgang Böhme; Axel Hille; Daniel Jablonski; Melita Vamberger; Uwe Fritz (7 August 2017), "Hybridization patterns in two contact zones of grass snakes reveal a new Central European snake species", Scientific Reports, Nature, 7 (1): Article number: 7378, Bibcode:2017NatSR...7.7378K, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-07847-9, PMC 5547120, PMID 28785033
- ↑ Angela Julian (22 August 2017). "What does the re-classification of European grass snakes mean for our native grass snakes?". Amphibian and Reptile Groups of the UK. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ↑ "Smooth snake | The Wildlife Trusts". www.wildlifetrusts.org. Retrieved 19 January 2023.
- ↑ Václav Gvozˇ dík, David Jandzik, Petros Lymberakis, Daniel Jablonski, Jirˇ í Moravec (2010). "Slow worm, Anguis fragilis (Reptilia: Anguidae) as a species complex: Geneticstructure reveals deep divergences". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 55 (2): 460–472. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.01.007. PMID 20079858. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Slow worm". Woodland Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ↑ "Common lizard". Woodland Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ↑ Rhodin 2011, p. 000.174
- ↑ Rhodin 2011, p. 000.172
- 1 2 3 Inns, Howard (2009) Britain's Reptiles and Amphibians, Wildguides.
- ↑ "Olive ridley turtle found injured off Seaford beach". BBC News. 19 January 2020. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ Rhodin 2011, p. 000.183
- ↑ Wildlife of Britain The Definitive Visual Guide. Dorling Kindersley. 2011. p. 168. ISBN 978-1-4053-6709-7.
- ↑ "Terrapin". Canal & River Trust. 11 May 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ "Common Wall Lizard". Surrey Amphibian and Reptile Group (SARG). Archived from the original on 5 January 2017. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ↑ Amphibians and Reptiles. HarperCollins. 2000. ISBN 978-0-00-220083-7.
- ↑ "Wild snake caught on film in north Wales". BBC. 16 May 2006.
- ↑ Loeb, Josh (2 September 2010). "Feature: 'The Camden Creature' - An amphibian and reptile trust says our waterways are alive with some exotic creatures". Islington Tribune. Archived from the original on 5 September 2010.
- ↑ "Britain's biggest snake - missing from UK for 10,000 years - now back and breeding". Daily Mirror. 11 May 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ↑ Julian, Angela (8 March 2021). "Enter the Natrix: surveying grass snakes in eastern England by Steve Allain". ARG UK. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
Notes
- ↑ Previously referred to as Natrix natrix helvetica[2][3]
External links
- British Reptiles from wildlifetrust.org.uk
- RAUK Identification Guide
- Rhodin, Anders G.J.; van Dijk, Peter Paul; Inverson, John B.; Shaffer, H. Bradley; Roger, Bour (31 December 2011). "Turtles of the world, 2011 update: Annotated checklist of taxonomy, synonymy, distribution and conservation status" (PDF). Chelonian Research Monographs. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 January 2012.
- Wilkinson, J.W., Baker, J. and Foster, J. Priorities for Non-Native Amphibians and Reptiles in the UK. ARC Research Report 11/02.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.