 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
1,2,4-Benzenetricarboxylic acid; 4-Carboxyphthalic acid; 1,2,4-Tricarboxybenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.667 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O6 | |
| Molar mass | 210.141 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 221–222 °C (430–432 °F; 494–495 K)[1] |
| 21 g/L (0.1M) at 25 °C | |
| log P | 2.721 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
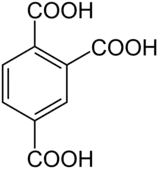
Trimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H3(СООН)3. Like the other isomers of benzenetricarboxylic acid, trimellitic acid is a colorless solid. It is prepared by oxidation of 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene.[2]
Isomers
- Hemimellitic acid (benzene-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid)
- Trimesic acid (benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid)
See also
References
- ↑ Fishwick, Brian (1957). "233. The analysis of mixtures of benzene-carboxylic acids by partition chromatography". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 1196. doi:10.1039/JR9570001196.
- ↑ Park, Chang-Man; Sheehan, Richard J. (2000). "Phthalic Acids and Other Benzenepolycarboxylic Acids". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.1608200816011811.a01. ISBN 0471238961.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.