| Hakea wattle | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. hakeoides |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia hakeoides | |
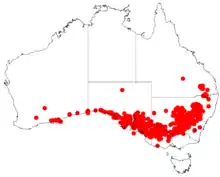 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Acacia hakeoides, known colloquially as hakea wattle, hakea-leaved wattle, or western black wattle is a species of Acacia native to southern Australia.[1][2] It can be found growing in sandy soils in semiarid and Eucalyptus woodland in the region.[3]
It typically grows to a height of 1.5 to 3.0 metres (5 to 10 ft) and produces yellow flowers from August to October.[3]
The seed of acacia hakeoides is edible and it has been suggested that this seed is suitable for culinary use as a flavouring agent, as a stable carbohydrate or as a coffee substitute, among others.[4] In light of this fact, the species has been listed by one study as a medium priority species of interest for domestication for seed production purposes.[4]
References
- 1 2 "Acacia hakeoides A.Cunn. ex Benth". World Wide Wattle. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ↑ Harden GJ (1990). "Acacia hakeoides A.Cunn. ex Benth". Plantnet - New South Wales Flora Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Sydney. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- 1 2 "Acacia hakeoides", Flora of Australia, retrieved 28 February 2022
- 1 2 McDonald MW, Maslin BR, Thomson LA (2002). "Domestication of wattles with edible seeds for the wheatbelt of Western Australia" (PDF). Conservation Science W. Aust. 4 (3): 170–180. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.