 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LSM-775, N-Morpholinyllysergamide, Lysergic acid morpholide |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
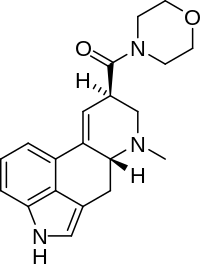
| Formula | C20H23N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 337.423 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
N-Morpholinyllysergamide (LSM-775) is a derivative of ergine.[2] It is less potent than LSD but is reported to have some LSD-like effects at doses ranging from 75 to 700 micrograms and a shorter duration. There are fewer signs of cardiovascular stimulation and peripheral toxicity with LSM-775 compared to LSD.[3]
See also
- 1cP-LSD
- 1B-LSD
- 1P-ETH-LAD
- 1P-LSD
- 1V-LSD
- ALD-52
- AL-LAD
- ETH-LAD
- Lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide (LSZ)
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
- O-Acetylpsilocin (4-AcO-DMT)
- PRO-LAD
References
- ↑ "Arrêté du 20 mai 2021 modifiant l'arrêté du 22 février 1990 fixant la liste des substances classées comme stupéfiants" [Order of May 20, 2021 amending the order of February 22, 1990 setting the list of substances classified as narcotics]. www.legifrance.gouv.fr (in French). 20 May 2021.
- ↑ Gogerty JH, Dille JM (July 1957). "Pharmacology of d-lysergic acid morpholide (LSM)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 120 (3): 340–8. PMID 13476356.
- ↑ Shulgin A, Shulgin A. "TiHKAL #26, LSD-25". Erowid.
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.