| NGC 6000 | |
|---|---|
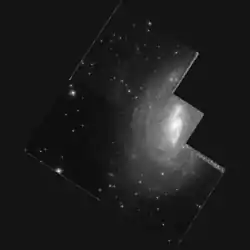 NGC 6000 as seen through the Hubble Space Telescope | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Right ascension | 15h 49m 49.5s |
| Declination | −29° 23′ 13″ |
| Redshift | 0.007315±0.000003 |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 2193±1 km/s |
| Galactocentric velocity | 2140±2 km/s |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.27 +/- 0.09 |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | -20.89 +/- 0.36 |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SB(s)bc |
| Apparent size (V) | 1.90′ × 1.6′ |
| Other designations | |
| ESO 450-20, MCG -5-37-3, IRAS15467-2914 and PGC 56145 | |
References: NASA/IPAC extragalactic datatbase, http://spider.seds.org/, http://cseligman.com | |
NGC 6000 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Scorpius. It is designated as SB(s)bc in the galaxy morphological classification scheme and was discovered by John Herschel on 8 May 1834. The galaxy is approximately 103 million light-years away. It is the brightest of all the galaxies in the constellation Scorpius.[1][2][3]
Two supernovae have been observed in this galaxy, namely 2007ch and 2010as, each having a magnitude of about 17.2 and 15.5 respectively.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Object No. 1 - NGC 6000". NASA/IPAC extragalactic database. NASA/IPAC. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ↑ "Revised NGC Data for NGC 6000". Seds. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ↑ "NGC 6000 (= PGC 56145)". cseligman. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
- ↑ "List of Supernovae". cbat.eps.harvard.edu. IAU Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. Retrieved 3 October 2015.
External links
 Media related to NGC 6000 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to NGC 6000 at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.