 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5,5′-(1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-diylidene)di(1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione) | |
| Other names
Lithol, Fast Yellow 1840 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.399 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H9N5O6 | |
| Appearance | orange solid |
| Density | 1.742 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
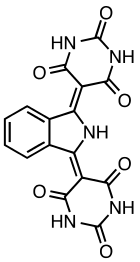
Pigment yellow 139 is an organic compound that is used as a yellow-orange pigment. It is classified as a derivative of isoindoline. This yellow-orange solid is virtually insoluble in most solvents.[1]
It is prepared by addition of ammonia to phthalonitrile to give diiminoisoindole, which in turn condenses with barbituric acid.[2]
References
- ↑ K. Hunger. W. Herbst "Pigments, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_371
- ↑ Volker Radtke, Peter Erk andBenno Sens "Isoindoline Pigments" in Edwin B. Faulkner, Russell J. Schwartz in High Performance Pigments. Edited by Edwin B. Faulkner and Russell J. Schwartz, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. 2009. doi:10.1002/9783527626915.ch14
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pigments.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.