 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
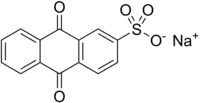
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium 9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-sulfonate | |
| Other names
Sodium 2-anthrachinonesulphonate; 2-Anthraquinone sodium sulfonate; Silver salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.555 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H7NaO5S | |
| Molar mass | 310.25 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Sodium 2-anthraquinonesulfonate (AMS) is a water-soluble anthraquinone derivative. In the laboratory it could be prepared by sulfonation of anthraquinone.[1]
Digester additive in papermaking
AMS is used as a catalyst in production of alkaline pulping in the soda process. It goes through a redox cycle similar to that of anthraquinone to give a catalytic effect. AMS was discovered as an efficient pulping catalyst before anthraquinone,[2] but has a higher cost.
References
- ↑ "Synthesis of sodium anthraquinone-2-sulfonate". PrepChem.com - Preparative chemistry procedures. Retrieved 2016-01-11.
- ↑ "Anthraquinone/ alkali pulping. A literature review" (PDF). July 1978.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.