 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
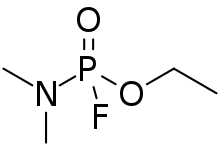
| IUPAC name
Ethyl dimethylphosphoramidofluoridate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11FNO2P | |
| Molar mass | 155.109 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Highly toxic |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
2.5 mg/kg (mice, intraperitoneal)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Fluorotabun is a highly toxic organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series. It's the fluorinated analog of tabun, i.e. the cyanide group is replaced by a fluorine atom.[2]
GAF is considered an ineffective GA-like agent. It is less effective than GAA.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "ChemIDplus".
- ↑ Ellison, D. Hank (2007). Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC. ISBN 9780849314346.
- ↑ "Investigation of chemical warfare installations in the Munsterlager area, including Raubkammer - Digital Collections - National Library of Medicine". collections.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-10-28.
| Animal toxins | |
|---|---|
| Bacterial | |
| Cyanotoxins | |
| Plant toxins | |
| Mycotoxins | |
| Pesticides | |
| Nerve agents | |
| Bicyclic phosphates | |
| Cholinergic neurotoxins |
|
| Other | |
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||
| Release (modulators) |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.