 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Bromo-1-phenylethan-1-one | |
| Other names
2-Bromo-1-phenylethanone 2-Bromoacetophenone α-Bromoacetophenone Bromomethyl phenyl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.659 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H7BrO | |
| Molar mass | 199.047 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Melting point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 136 °C (277 °F; 409 K) 18 mm Hg[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Toxic(T) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
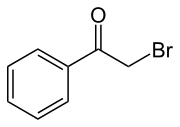
Phenacyl bromide is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH2Br. This colourless solid is a powerful lachrymator as well as a useful precursor to other organic compounds.
It is prepared by bromination of acetophenone:[2]
- C6H5C(O)CH3 + Br2 → C6H5C(O)CH2Br + HBr
The compound was first reported in 1871.[3]
References
- 1 2 Phenacyl Bromide, TCI America
- ↑ R. M. Cowper and L. H. Davidson. "Phenacyl bromide". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 2, p. 480
- ↑ A. Emmerling and C. Engler (1871). "Ueber einige Abkömmlinge des Acetophenons". Ber. 4 (1): 147–149. doi:10.1002/cber.18710040149.
External links
 Media related to Phenacyl bromide at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Phenacyl bromide at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.